Modulation is used to modulate baseband signal. Basically it is a technique used to generate a strong signal from a weak signal with help of a transporter signal known as carrier signal.
A baseband signal is main source of any signal. It can be a sinusoidal wave or discrete pulse. In communication a baseband signal need to traverse long distance, but it become weak with respect to distance so that we need to add a carrier which carry the base band signal and send baseband signal to destination.
A baseband signal pass through a modulator with carrier frequency then transmission starts, on other side demodulator demodulate signal and receive the original signal.
Practical example: If we through a paper it will traverse some distance but if we through it along with a stone it will traverse more distance. Here paper is baseband signal and stone is carrier.
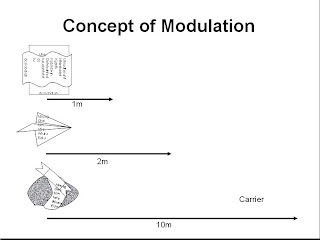 |
| Basic signal modulation concept with carrier frequency |
There are three basic
type of Modulation schemes which are describe below:
1. Analogue Modulation
2. Digital Modulation
3. Pulse Modulation
Analogue Modulation:
1. Analogue Modulation
2. Digital Modulation
3. Pulse Modulation
Analogue Modulation:
This modulation scheme
works with analogue signal (continuous signal varies in time) to traverse
forward.
AM:Amplitude Modulation
FM:Frequency Modulation
PM:Phase Modulation
Digital Modulation:
This modulation scheme
works with digital signal (discrete signal)
ASK:Amplitude Shift Keying
FSK:Frequency Shift Keying
PSK:Phase Shift Keying
Pulse Modulation:
This modulation scheme
works with pulse wave.
PAM:Pulse Amplitude Modulation
PFM:Pulse Frequency Modulation
PPM:Pulse Position Modulation
PWM:Pulse Width Modulation
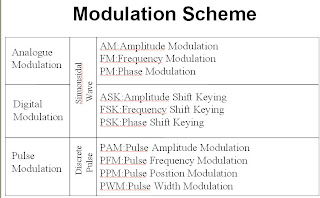 |
| Different Modulation Schemes |
Amplitude Modulation Equation for Baseband Signal in
frequency domain is:-
S(t)=[1+
mg(t)]c(t)
=A[1+ mg(t)] cos(wct)
A = Amplitude
m = Modulation Index
g(t) = Baseband Signal
wc = Angular Frequency (rad/sec)
Frequency Modulation Equation:
s(t) = A cos Ø(i)t
Where Ø(i)t is instantaneous phase
Comments
Post a Comment